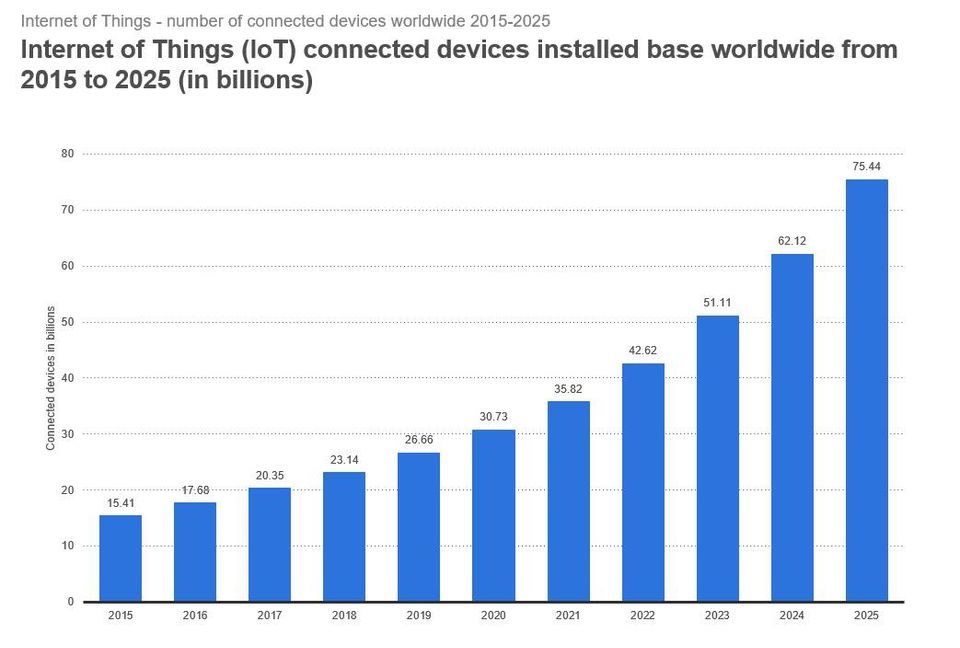
Smart devices are now cheaper than ever; through globalization and advancements in computing, smart devices have a higher value to cost ratio. There are currently 30 billion smart devices globally, expected to rise to 100 billion devices by 2027. We aim to capitalize on this market by utilizing the wasted idle computing power in these smart devices to create a vast, low-latency high-performance global computer, a Hyper Network, or HyperNet for short.
“If the cloud was yesterday and distributed computing is today, the HyperNet is tomorrow.” – Hypernet Team
Problems with traditional computing and cloud computing
- Data centers cannot keep up with the demands of modern technological advancements.
- The initial capital required to build data centers are only available to large companies with large amounts of capital; this creates an unfair advantage to the average everyday developer with limited capital.
- We are all surrounded by computers that have unused computational power and resources. Traditional computing utilizes enterprise hardware that relies on bulk purchases to remain cheap (economies of scale), further increasing the initial capital cost and wasting vast amounts of untapped consumer computing power.
- High-latency. Cloud providers and traditional computing work well in developed and some emerging countries where market growth is high and consistent. Companies create data centers in those regions, meaning that outside those regions wants to use cloud computing; it has high latency and routine disconnects due to the distance between the user and data centers.
Why did we invest in HyperNet?
We diversify our investments among different use-cases for blockchain technology. We have targeted the overall health and wellbeing of the blockchain technology; to invest in solutions to problems that affect a broad audience. For example, the Marlin Protocol increases the performance and stability of the Networking layer of the blockchain, allowing for faster transactions per second without rebuilding core infrastructure. We believe that edge-computing is the future, and we are proud to apart of this project.
A few reasons for our investment:
- Hypernet works for almost all types of programs, whereas competitors focus on a more straightforward class of computing called “grid computing.”
- A sophisticated algorithm based on a distributed average consensus was designed from the ground up for dynamic, distributed, and decentralized networks of devices. The algorithm offers the right answer to buyers to buy efficiently and at a low cost.
- Hypernet distributes your computational workload across a cluster of internet-connected devices. It starts distributing them to the devices closest to you, which means that the system latency is low and highly scalable.
- The identification of bad actors allows for the system to remain reliable and recalculate computation and distribution if devices are added or removed.
How does this support the blockchain ecosystem?
- To discourage malicious behavior, both buyers and sellers must stake collateral to join the network. The blockchain allows HyperNet to economically incentivize reliable performance and punish terrible behavior that is disruptive to the network.
- The blockchain allows for transaction data to be publicly available; this increases accountability and transparency in the system, resulting in a healthier computation marketplace.
- HyperTokens will allow buyers to pay sellers for their computing time. Market dynamics will allow for the prioritization of projects on the network.
- HyperNet’s reward system will allow for “good participants” to receive rewards for staying on the network regardless of their computational resources are being used or not. Allowing the system to scale a lot faster and incentivizes stability.
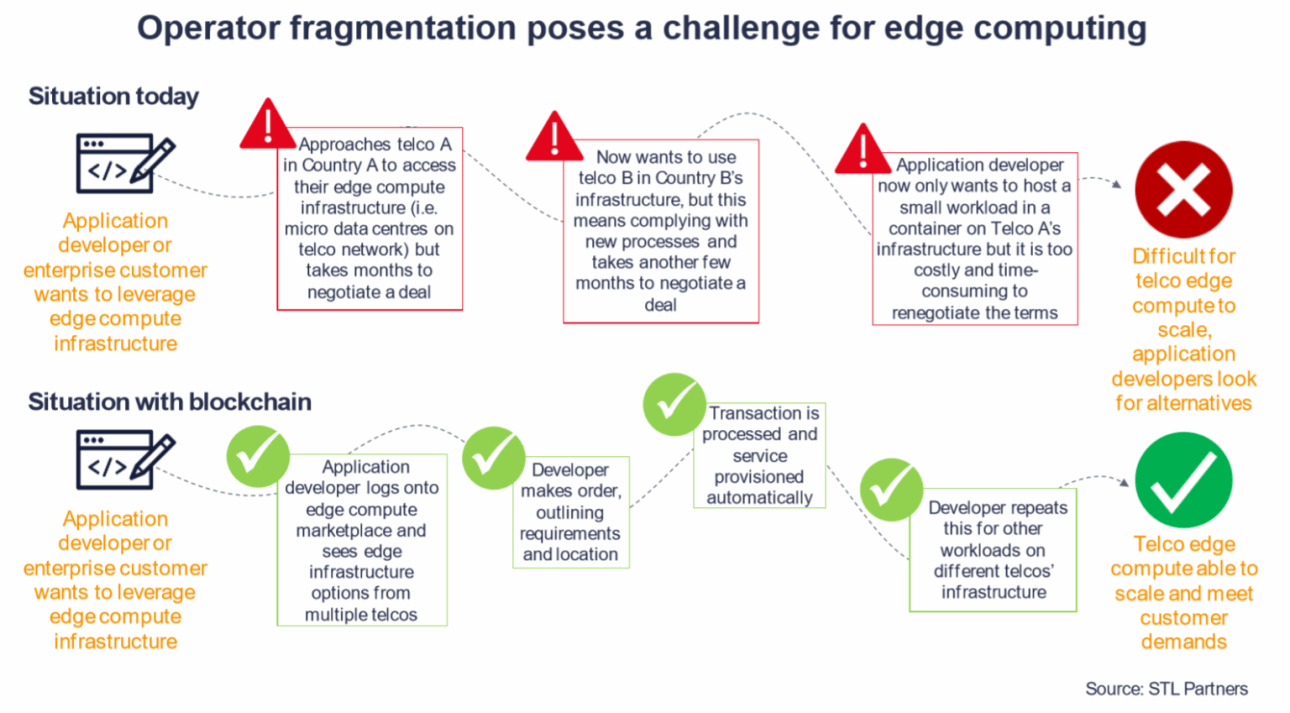
The blockchain isn’t just a buzzword; the blockchain and cryptocurrency are critical to a project like HyperNet as it allows anyone to participate in the market transparently.
HyperNet and 5G
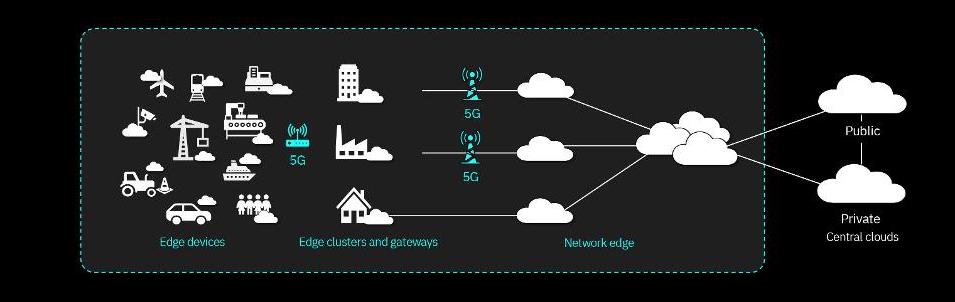
Governments are pushing IoT devices all over the world. With self-driving cars and the sharing economy rising rapidly, governments are trying to build the infrastructure to benefit significantly from these technologies. Enter 5G, 5G is designed for low latency data transmission at high rates; verses LTE, which was designed for long-range transmission. HyperNet has a much lower data latency at around 100ms, but this can be improved using 5G. Verizon, for example, clocked the latency of its earliest 5G network rollouts in Chicago and Minneapolis at less than 30 ms with regular cloud computing. With HyperNet, this number can reach 10-20ms in latency between devices. Over the long term, as 5G evolves, latency will drop to 1ms, allowing for near-instantaneous data transmission.
Capitalizing on the growing market
The edge computing market was valued at around $ 1.7 billion in 2017 and projected to reach $ 16.55 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR (Compound annual growth rate) of 32.8% from 2018 to 2025.
The most significant driver of IoT is the developing world; emerging nations are leapfrogging traditional development to achieve higher economic growth. High economic growth has led to a massive increase in the acquisition of smart devices. Being able to use those wasted computational resources while compensating individuals for their computational time is necessary to help develop those regions by offering an extra source of income for using the resources of their smart devices. Emerging markets tend to have a limited amount of data centers close by as they are seen as unprofitable regions by significant companies; this leads to more copious amounts of latency.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles bring together a wide variety of innovative technologies that generate, gather, and process large amounts of information about their surroundings. Autonomous cars won’t make it far from the garage before encountering latency and bandwidth challenges. This is due to a lack of low-latency solutions at its disposal; autonomous cars need to compute real-time data using their hardware to react fast enough. This lowers the amount of information that can be processed by the computational
Smart cities
Cities around the world are investing in exciting new technologies that could transform their transportation and communications infrastructure. Whether it takes the form of sensors designed to regulate traffic flow to reduce congestion or more sophisticated power grids that better regulate energy usage, smart city technology will fundamentally alter the way people interact with their urban environment.
IoT Healthcare
Edge computing offers five advantages over cloud computing: higher data transmission speed, less dependence on limited bandwidth; greater privacy and security; and lower costs; as more sensor-derived data is used locally, less data needs to be transmitted remotely.
The Team


